
ID the Future
Intelligent Design, Evolution, and Science Podcast

Latest Episodes

On the Origin of “Tall Blondes”: Correcting the Record on Giraffe Evolution
- 2178
- Wolf-Ekkehard Lönnig
- February 23, 2026

No Thinking Without a Thinker: Dr. Mihretu Guta on Consciousness
- 2177
- Dr. Mihretu Guta
- February 20, 2026

Bioengineer Stuart Burgess Reads From New Book Ultimate Engineering
- 2176
- Stuart Burgess
- February 18, 2026

Rockets & Wristbones: Optimal Engineering in Biology
- 2175
- Stuart Burgess
- February 16, 2026

Douglas Axe: Dragonflies, Cookies, and Our Built-In Design Intuition
- 2174
- Douglas Axe
- February 13, 2026

Ultimate Engineering: An Interview with Bioengineer Stuart Burgess
- 2173
- Stuart Burgess
- February 11, 2026

The Accidental Inventor: An Interview with Hal Philipp
- 2172
- Hal Philipp
- February 9, 2026

How Life Leverages the Laws of Nature to Survive
- 2171
- Howard Glicksman
- February 6, 2026

Mind and Soul at the Threshold of Death
- 2170
- Michael Egnor, Alexander Batthyany
- February 4, 2026
Topics
__edited __repeat Intelligent Design Evolution Darwinism Materialism Neo-Darwinism Natural Selection Charles Darwin origin of life Atheism irreducible complexity biology abiogenesis DNA Theism Casey Luskin fine tuning theistic evolution Richard Dawkins Darwinian Evolution Big Bang fine-tuning engineering Scientism Darwin Michael Behe Science and faith evolutionary theory teleology God genetics Evolutionary Biology common descent William Dembski multiverse Biological Information methodological naturalism Junk DNA cosmology science education Fossil Record Cambrian Explosion Proteins Academic Freedom Naturalism human evolution Stephen Meyer Philosophy philosophy of science Christianity physics mathematics human exceptionalism scientific racism Science information human origins chemical evolution Brian Miller Darwin Devolves Francis Collins Eugenics C.S. Lewis scientific revolution purpose Molecular Machines devolution Aristotle scientific Materialism Icons of Evolution history of science Kitzmiller v. Dover specified complexity systems biology Jonathan Wells Featured __video-only Stephen C. Meyer macroevolution Darwin's Doubt chemistry genetic information Microevolution Michael Egnor entropy astronomy Alfred Russell Wallace science and religion Religion Ethics Eric Metaxas engineering principles philosophical materialism Albert Einstein Theology Jerry Coyne Guillermo Gonzalez Free Will biochemistryNews
Podcast coverage and related news from Evolution News.
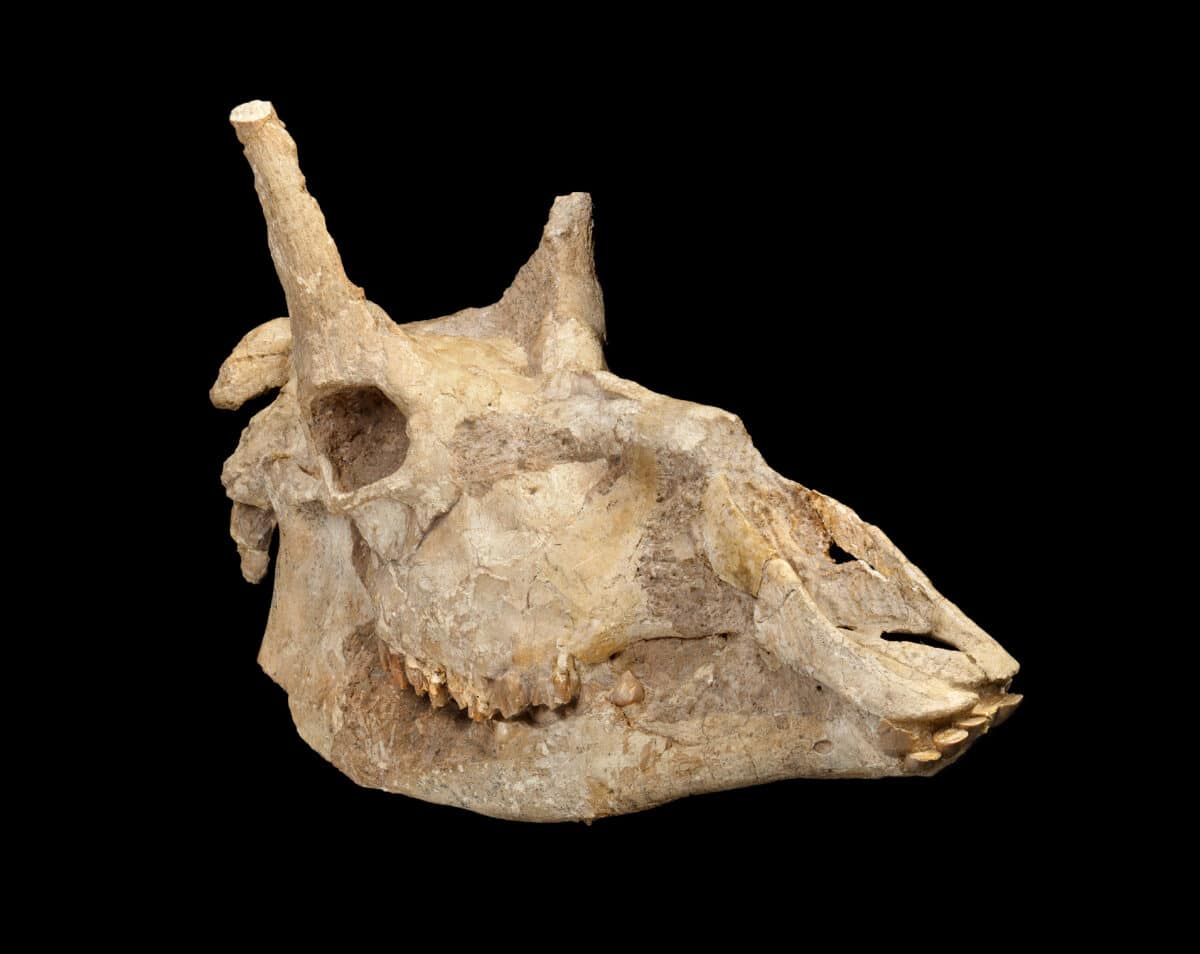

Giraffes and the Fossil Record: Bad News
- Andrew McDiarmid
- February 26, 2026
- 2
- Paleontology

Burgess: Examples of Body’s Ultimate Engineering
- Andrew McDiarmid
- February 20, 2026
- 2
- Anatomy

Is Life Intelligently Engineered? Ask an Engineer
- Andrew McDiarmid
- February 17, 2026
- 2
- Intelligent Design

The Design Intuition and Its Critics
- Andrew McDiarmid
- February 14, 2026
- 2
- Scientific Reasoning

Introducing Ultimate Engineering
- Andrew McDiarmid
- February 11, 2026
- 2
- Intelligent Design

How Life Leverages the Laws of Nature to Thrive
- Andrew McDiarmid
- February 7, 2026
- 2
- Intelligent Design
Terminal Lucidity Shows Indestructible Personhood
- Andrew McDiarmid
- February 2, 2026
- 3
- Neuroscience & Mind
Ingenious Cellular Structure that Keeps Us Alive
- Andrew McDiarmid
- February 1, 2026
- 2
- Intelligent Design

Irreducible Intelligence
- Andrew McDiarmid
- January 28, 2026
- 2
- Evolution

Intelligence Needed for Functional Information
- Andrew McDiarmid
- January 21, 2026
- 3
- Intelligent Design
